Screening for Anxiety and Depression

Screening for Anxiety and Depression
When to call it a disorder?
Characterized by a clinically significant disturbance in an individual’s cognition, emotional regulation, or behaviour.
Usually associated with distress or impairment in important areas of functioning (functional impairment).
Duration also have to be taken into consideration.
🔍Screening tools
DASS score
Used for screening of depression, anxiety and stress.
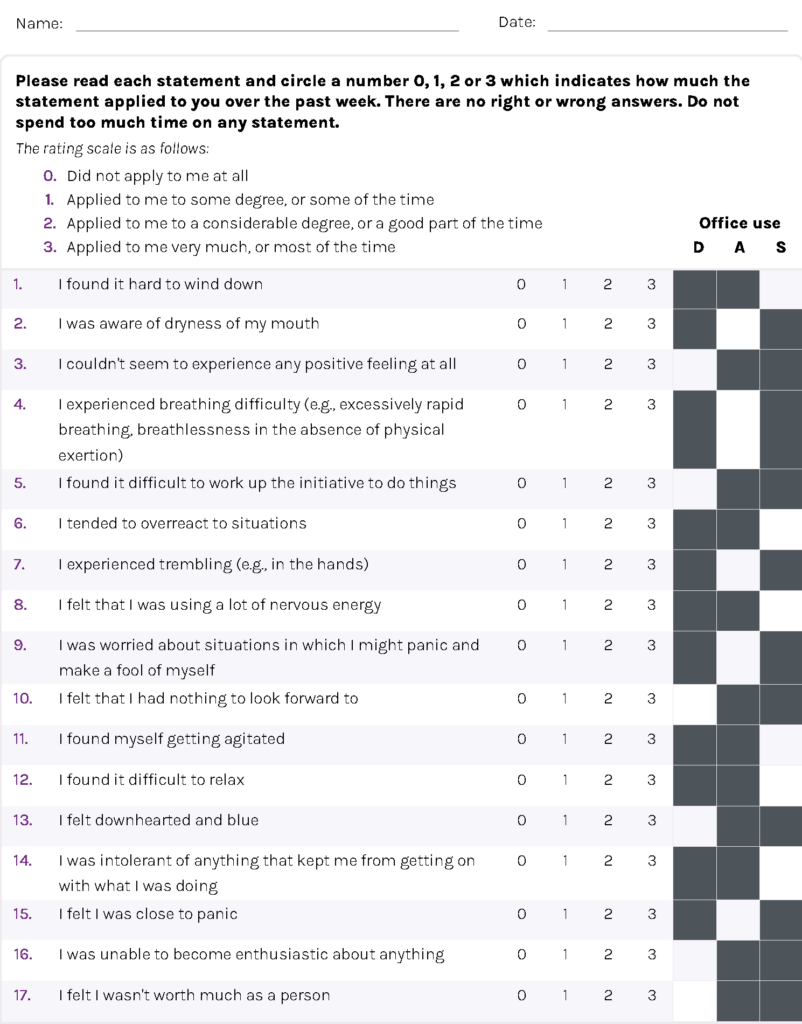
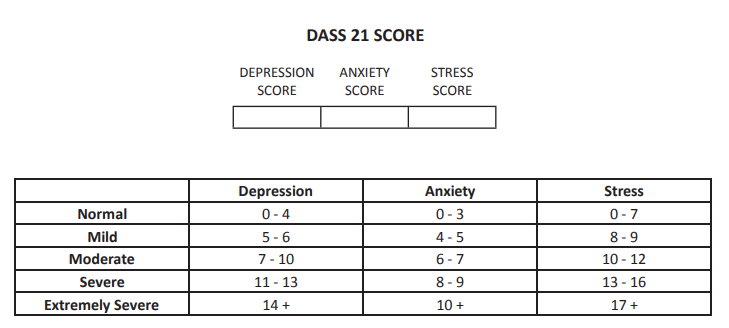
Once patient is suspected to have symptoms of depression or anxiety, further assessment can be done via more specific questionnaire e.g. GAD-7, PHQ-9
Anxiety disorders

Common physical symptoms:
- Chest discomfort
- Palpitations
- SOB
- Stomach upset
- Cold and clammy skin
Cognitive symptoms:
- Feeling worried
- Fear
- Think of impending doom

GAD diagnostic and severity measures
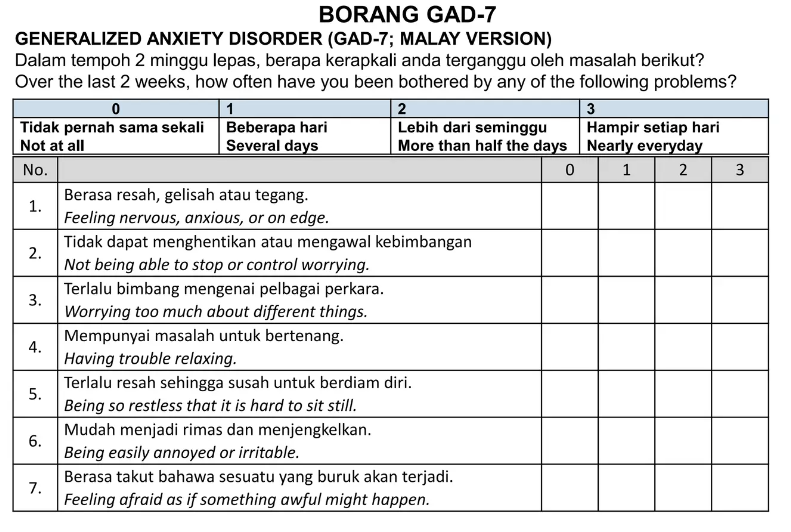
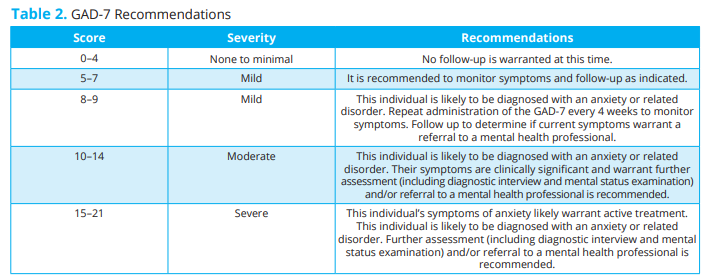
Source: PAR Staff (2020). Administration and Scoring of the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7) [technical supplement]. PAR.
It is important also to assess:
– Any underlying organic cause for the symptoms, e.g. ACS, asthma, hyperthyroid, etc.
– Substance misuse (either as a comorbid or complication of anxiety)
Major Depressive Disorder
DSM-5 Diagnostic Criteria:
5 or more of the following symptoms must be present nearly every day during a 2 week period:
Core symptoms (>= 1 required for diagnosis)
- Depressed mood most of the day
- Anhedonia or markedly decreased interest or pleasure in almost all activities
Additional symptoms
- Clinically significant weight loss or increase or decrease in appetite.
- Insomnia or hypersomnia
- Psychomotor agitation or retardation
- Fatigue or loss of energy
- Feelings of worthlessness or excessive or inappropriate guilt
- Diminished ability to think or concentrate, or indecisiveness
- Recurrent thoughts of death or suicidal ideation
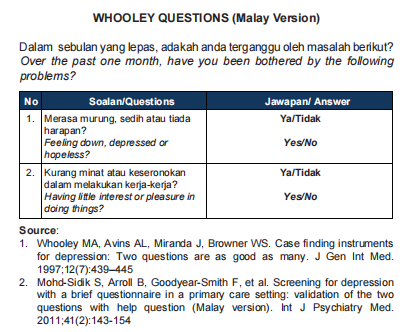
Fast screening tools for MDD
Consist of 2 questions to screen for depression
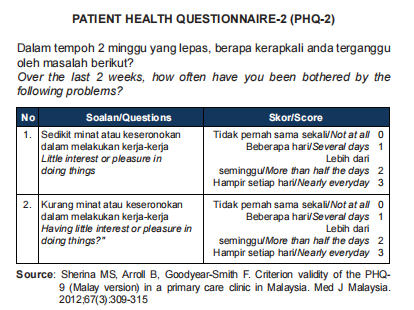
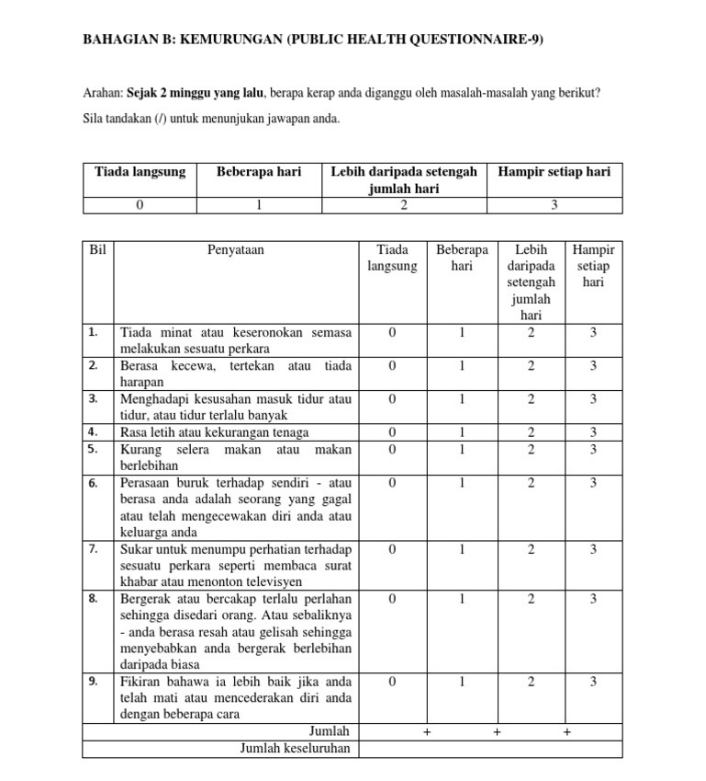
Depression diagnostic and severity measure (PHQ-9)
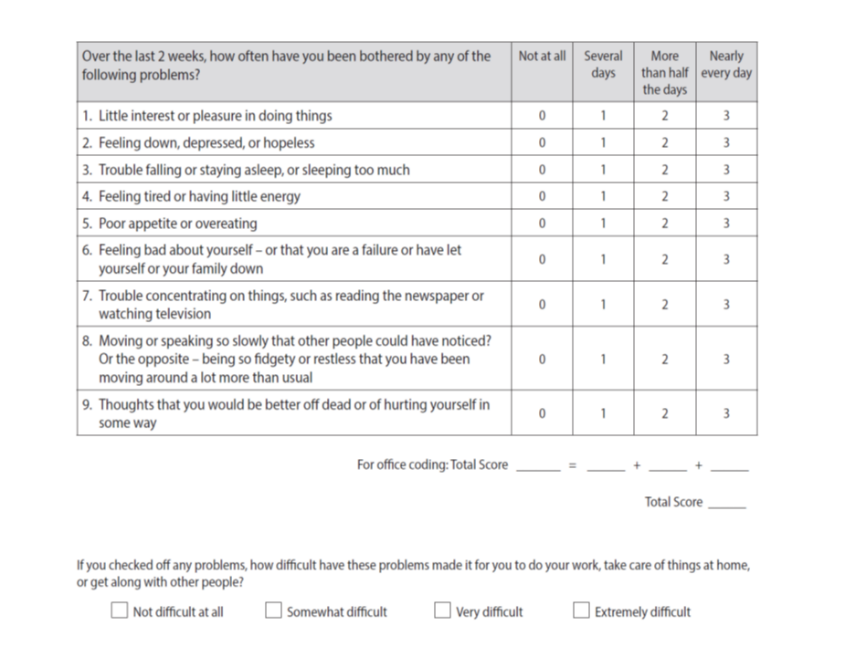
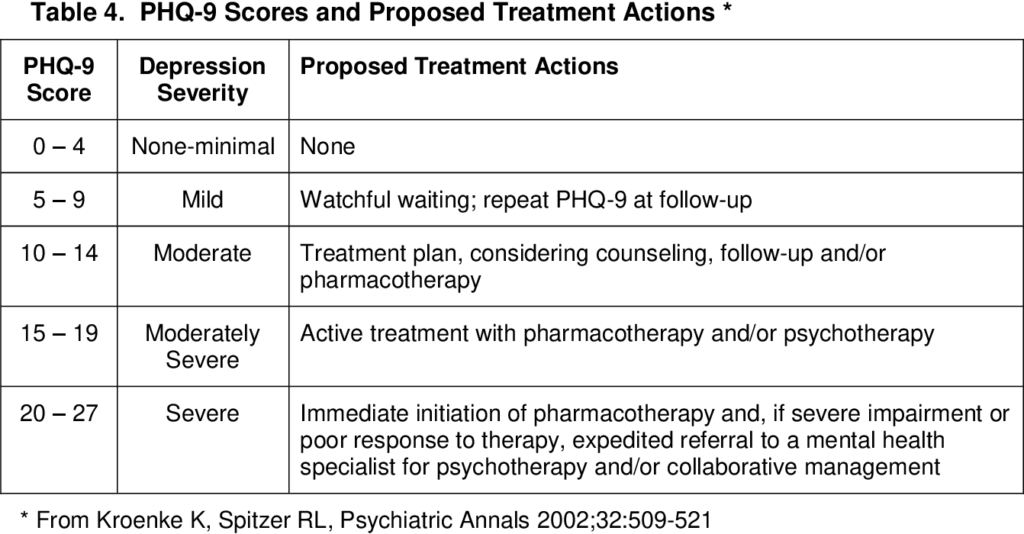
Remember to assess:
– Manic symptoms – TRO bipolar
– Suicidal thoughts/ideation/attempt
– Psychosis
– Substance abuse/usage
– Underlying medical illness that may contribute to the symptoms
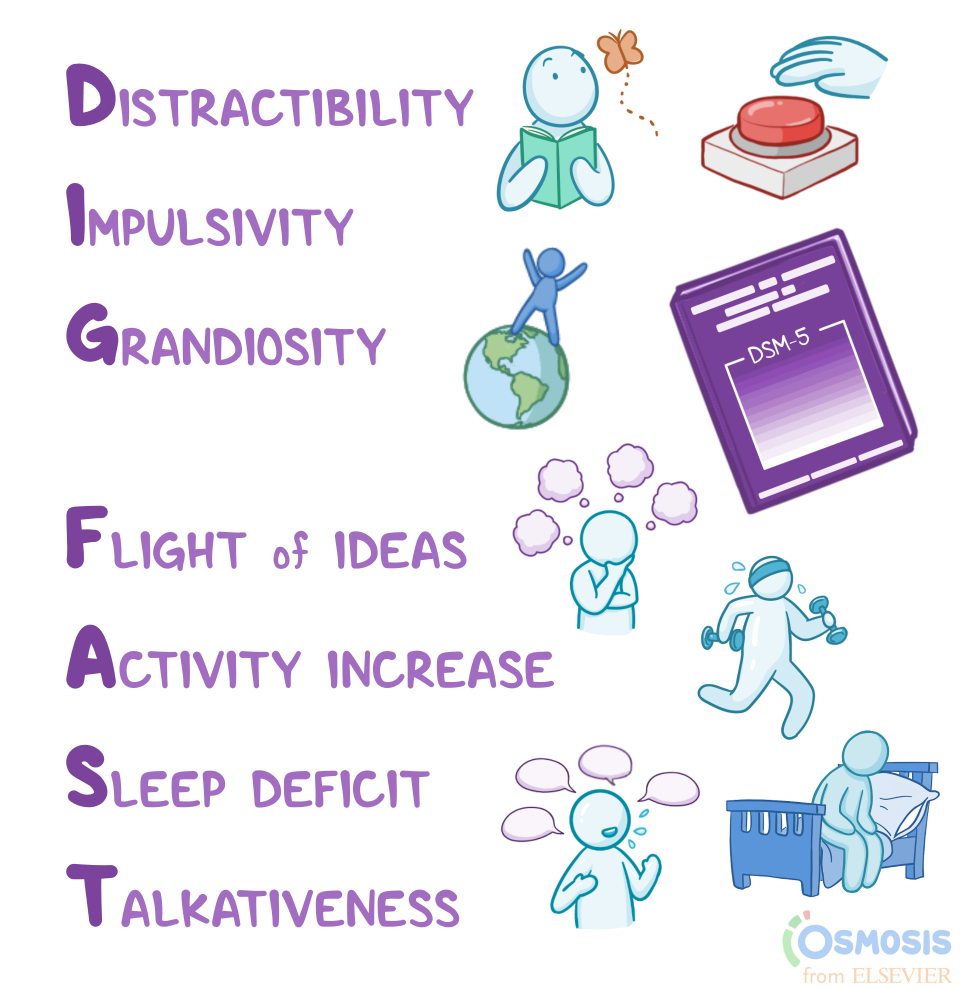
Mania vs Hypomania (Difference in symptoms duration)
3 or more of manic symptoms
Mania: at least 1 week or more
Hypomania: at least 4 days but less than 1 week.
🚑 Indications for referral
- Unsure of diagnosis
- Attempted suicide
- Active suicidal ideas
- Failure of treatment
- Advice on further treatment
- Clinical deterioration
- Recurrent episode within one year
- Psychotic symptoms
- Severe agitation
- Self neglect


