Acne Vulgaris
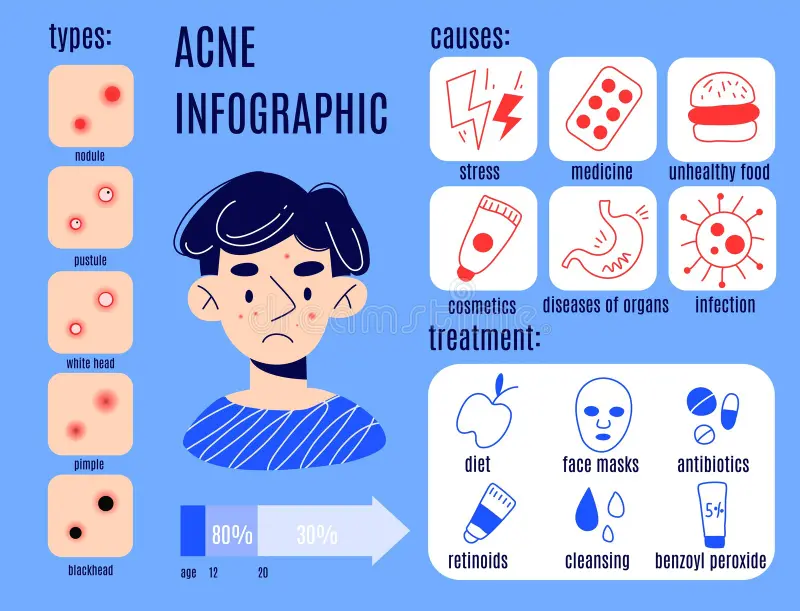
Acne Vulgaris
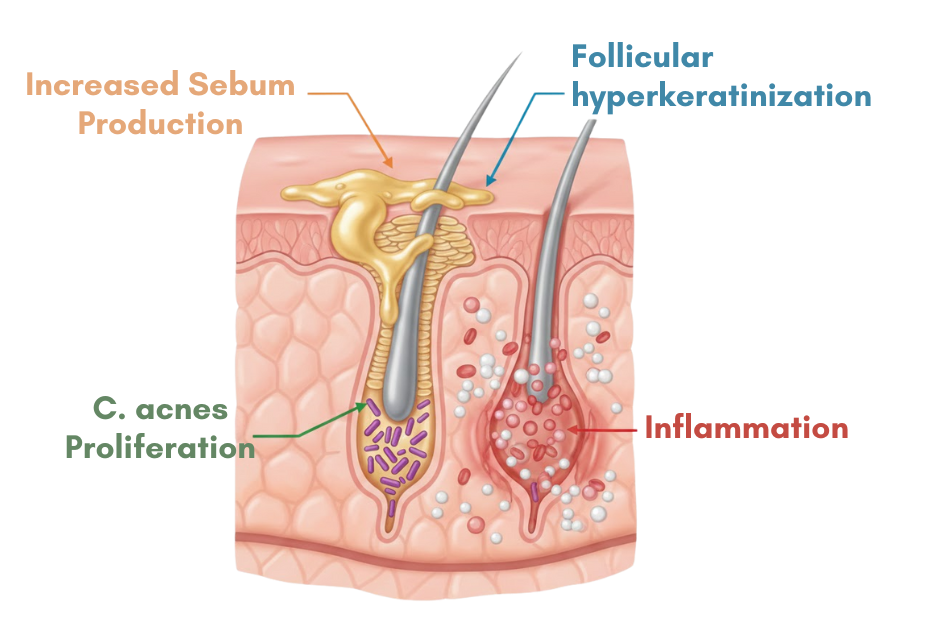
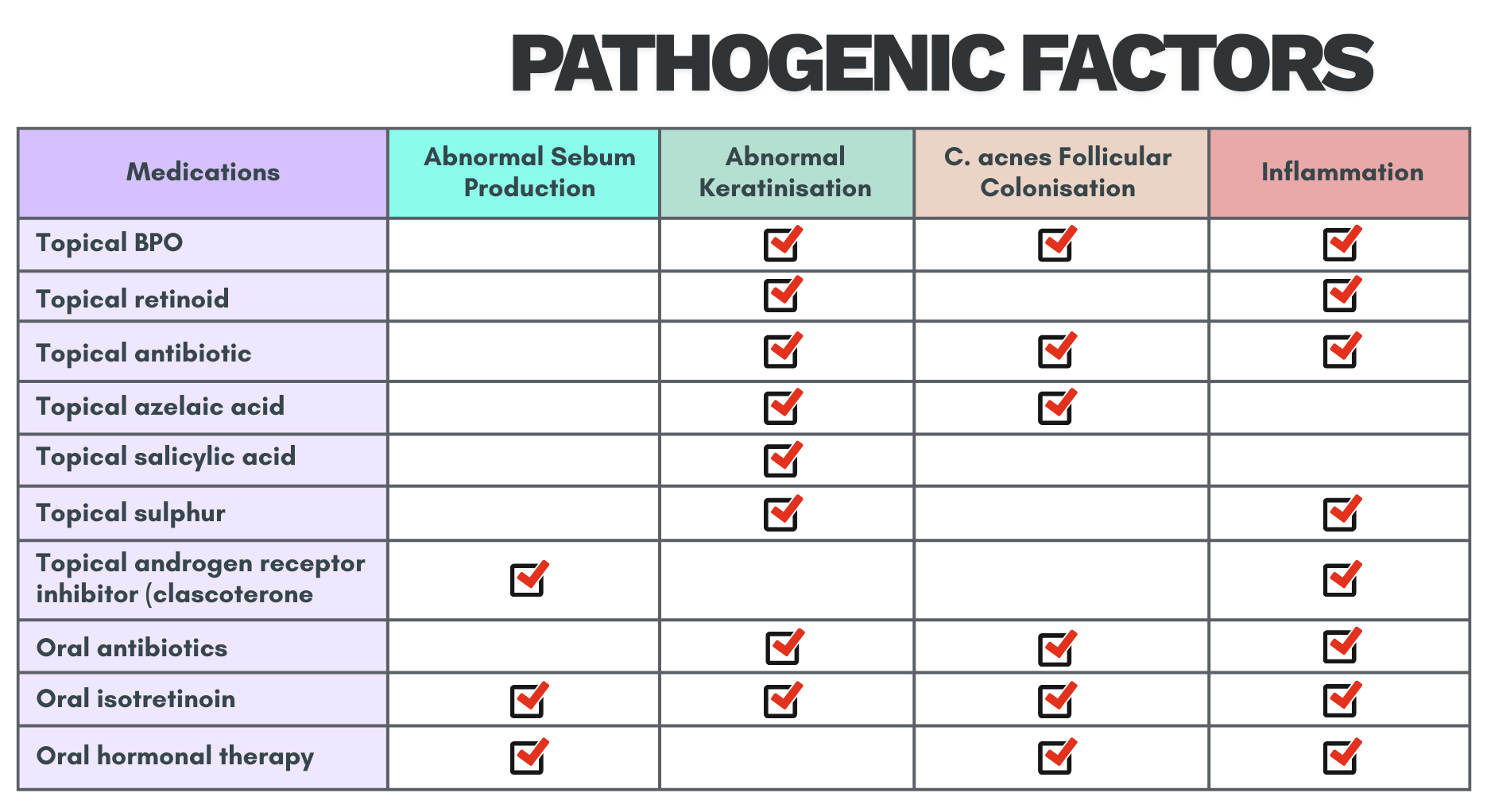
Pathogenesis
Involves 4 key pathogenic factors
- Increased sebum production
- Altered follicular keratinization leading to comedones formation
- Follicular colonization by Cutibacterium acnes (C. acnes), previously known as Propionibacterium acnes
- Inflammation around pilosebaceous unit
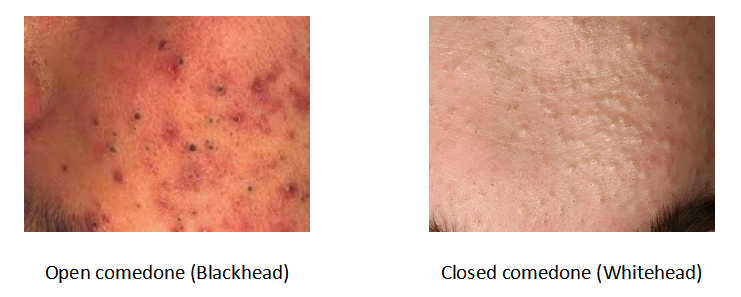
Clinical presentation
Non-inflammatory lesion (NIL): open (blackheads) & closed (whiteheads) comedones
- Open comedones (blackheads) have dilated follicular opening, where the keratin plug darkens due to oxidized lipid and melanin.
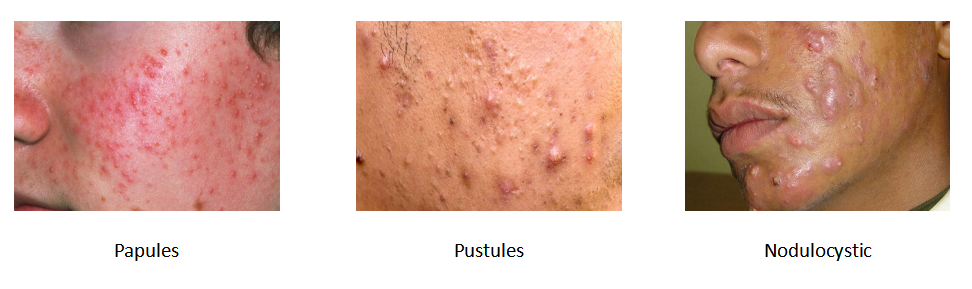
Inflammatory lesion (IL): papules, pustules, nodules & cysts
Comedone
Inflammatory lesions
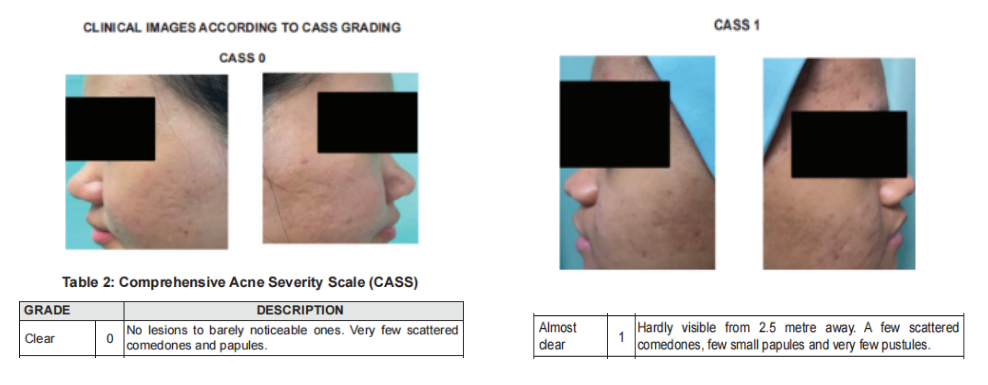
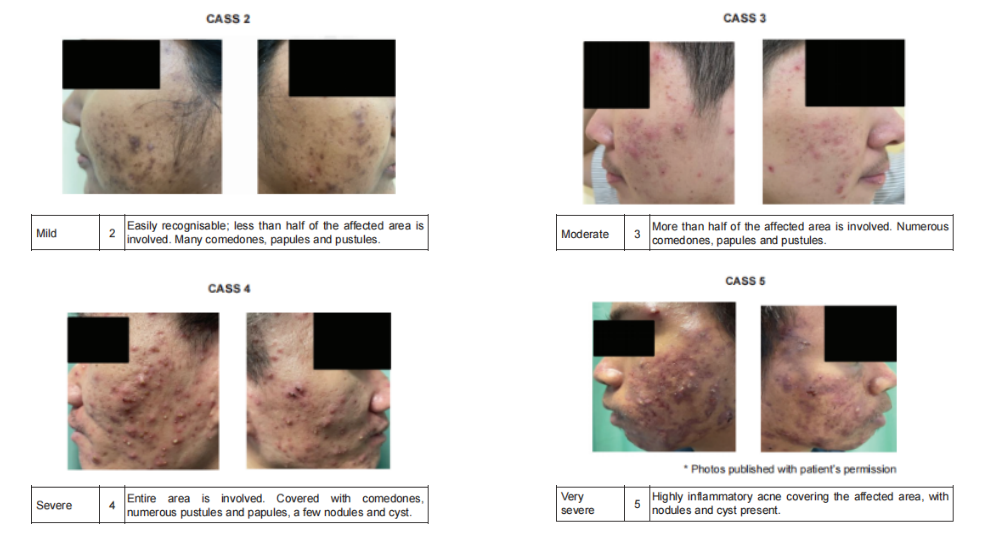
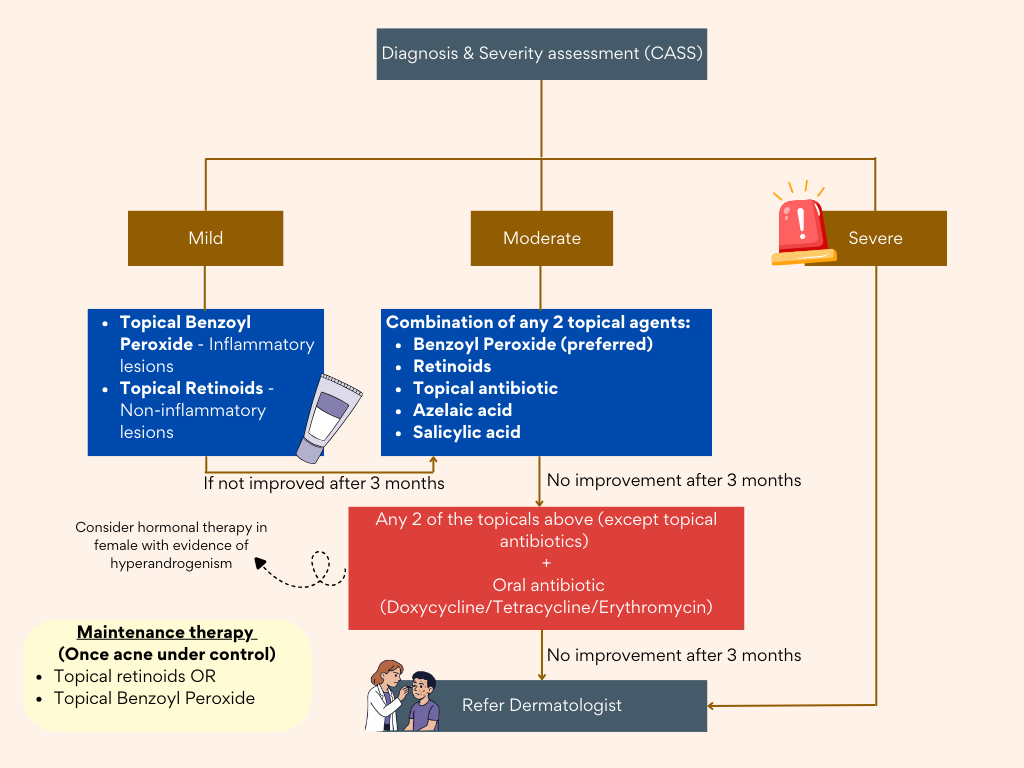
Severity assessment
Using the Comprehensive Acne Severity Scale (CASS)
Treatment (topical) – Mainstay
Commonly used:
- Topical Benzoyl Peroxide (BPO)
- Topical Retinoids
- Topical Antibiotics
- Fixed Combination Therapy
Topical agents are the mainstay of treatment in mild-moderate acne vulgaris.
The commonly used agents are topical BPO, retinoids, Abx & fixed combination preparations.
Combination treatment with either topical BPO, retinoids or topical Abx is more effective than monotherapy
Topical Benzoyl Peroxide (BPO)
- Available in 2.5%, 5% & 10% concentrations
- Topical BPO monotherapy or in combination with other topical therapy should be given in mild to moderate acne vulgaris.
- Practical advice on topical BPO:
– Start at lower concentration of 2.5% & titrate gradually to 5 – 10% if no improvement.
– Apply once daily on affected areas only. (May increased up to twice daily if needed)
– If skin irritation develops, withhold treatment & restart on alternate days once AE has subsided.
– Concomitant use of moisturizer may improve tolerability.
– Bleaching of clothes may occur & the pt should be advised accordingly.
Topical retinoids (synthetic derivatives of Vitamin A)
- Include tretinoin, adapalene, tazarotene & isotretinoin.
- In Malaysia, only topical tretinoin & adapalene are currently available.
- Topical retinoids (e.g. tretinoin & adapalene) monotherapy should be used in non-inflammatory acne vulgaris or in combination with other therapies in inflammatory acne vulgaris.
- Contraindicated in pregnancy
- Practical advice:
– It can cause photosensitivity, thus should be applied at night.
– Apply a thin layer on the affected areas or the entire face.
– If skin irritation develops, withhold treatment & restart on alternate days once the AE has subsided.
– Concomitant use of moisturiser may improve tolerability.
– Adequate sun protection (e.g. using broad-spectrum sunscreen, umbrella or hat) is advisable.th other topical therapy should be given in mild to moderate acne vulgaris.
Topical Antibiotics
- Useful in treatment of mild-moderate inflammatory acne.
- The use of topical Abx as monotherapy should be avoided to prevent bacterial resistance.
- Topical clindamycin & erythromycin are the most widely prescribed Abx. (Only topical clindamycin is available in Malaysia for the treatment of acne).
Fixed combination therapy
Available options:
Clindamycin/BPO ; Adapalene/BPO ; Erythromycin/BPO ; Clindamycin/Tretinoin
Other topical agents
- Topical Azelaic Acid (anti-microbial & anti-comedonal properties)
– Also inhibits tyrosinase, thus effective for post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation - Topical Salicylic Acid (keratolytic & comedolytic effects)
Treatment (systemic)
- Oral antibiotics
- Oral isotretinoin (prescribed only by dermatologist)
- COCP (may be beneficial in female patient especially those with hyperandrogenism)
- Spironolactone (anti-androgen & aldosterone antagonist) – competes with DHT for androgen receptors in the skin
- Metformin (may be beneficial as adjuvant treatment; enhances insulin sensitivity –> reduce androgenic hormone)
Oral antibiotics
- Indicated for moderate-severe papulopustular/inflammatory acne vulgaris.
- Topical retinoid, BPO or AA should be used after discontinuation of Abx.
- Commonly used:
– Tetracycline group (1st line) – contraindicated in pregnancy, lactation, age < 8 y/o or allergic to tetracyclines.
– To reduce the AE of doxycycline, pt should be advised to take medication after meal with plenty of water; practice adequate sun protection.
– Macrolides (Erythromycin, Azithromycin)- safe to be used in pregnancy & lactation
– Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Co-trimoxazole) – should only be used when other Abx have failed or are contraindicated because of its potential serious AEs. - Oral abx in combination with other topical treatment e.g. BPO, retinoid & AA is advocated as it prevents development of bacterial resistance, achieves faster resolution of lesions & targets multiple pathogenesis of acne.
- Oral doxycycline, tetracycline or erythromycin should be used for moderated to severe acne vulgaris.
- Response to these Abx should be evaluated at 6 – 8 weeks.
- Target duration therapy should not exceed 3 – 4 months to reduce resistance.
Oral isotretinoin
- Reduces sebaceous glands activity & size markedly, normalises follicular keratinisation, indirectly inhibits C. acnes growth in hair follicle & exerts an anti-inflammatory action.
- Should be prescribed for nodulocystic or severe acne vulgaris & treatment-resistant moderate acne vulgaris.
- Should only be prescribed by dermatologists
- Teratogenic & strict contraceptive practice is required for females who may become pregnant.
Cosmeceuticals
- May be used as an adjunct in the management of acne vulgaris.
- However, stronger evidence is warranted before cosmeceuticals can be recommended.
- Types: cleanser, sonic cleansing device, moisturiser, sunscreen (UVB cause inflammation, increase sebum production & proliferation of keratinocytes), hydrocolloid acne patches
- Active ingredients in Cosmeceutical for Acne Vulgaris:
– Comeolytics – e.g. retinaldehyde, retinol. AHA (e.g. GA), beta-hydroxy acids (e.g. salicylic acid) & polyhydroxy acids (e.g. lactobionic acid & gluconolactone)
– Sebum controller with anti-inflammatory properties – e.g. nicotinamide/niacinamide
– Antibacterial agents – e.g. tyrothricin, tea tree oil, aloe vera, propolis, licochalcone A & cedar
– Antioxidant – e.g. Green tea extract
– Vitamin C (ascorbic acid)
Summary on mode of action of topical and systemic treatment
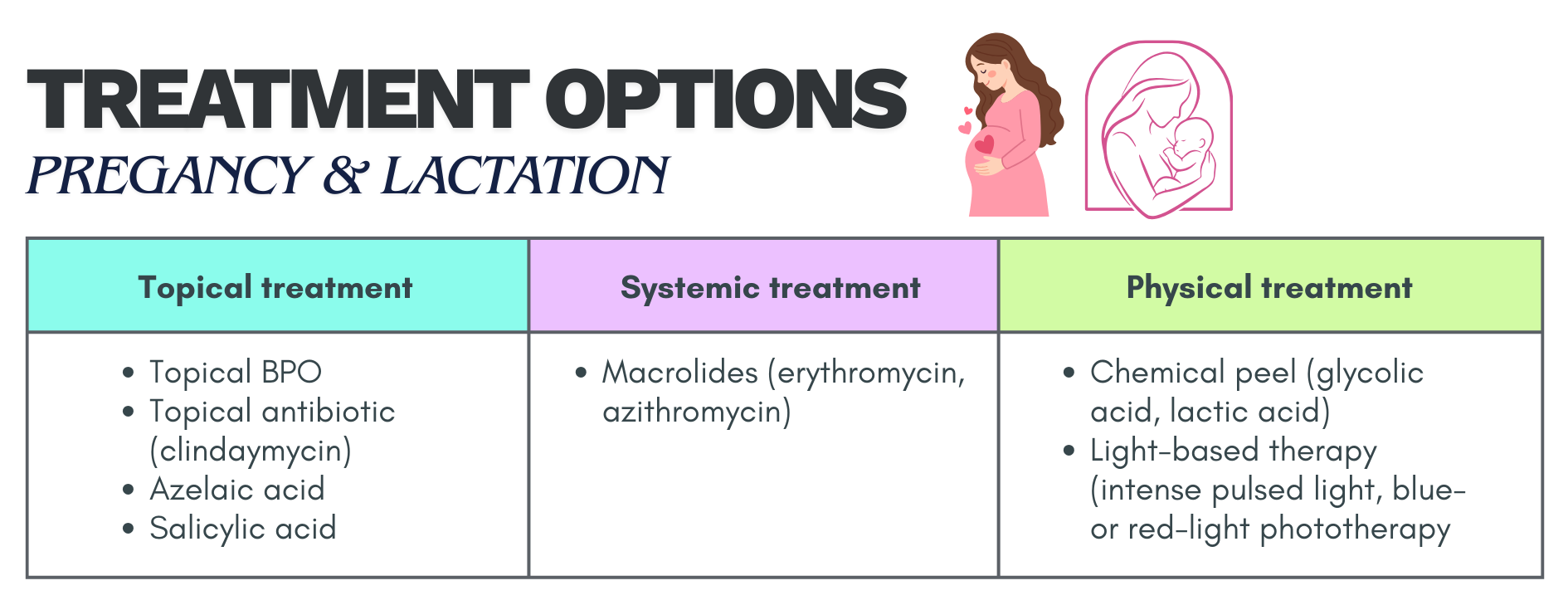
Management for special groups
Pregnant and lactating women
Hormonal therapy, tetracyclines, co-trimoxazole & isotretinoin should be avoided.
Adolescent
- Topical BPO & topical retinoids (tretinoin & adapalene) may be used safely in adolescents.
- Oral tetracycline derivatives (e.g. tetracycline, doxycycline, & minocycline) should not be used in patients aged < 8 y/o.
- Oral isotretinon can be used safely in patients ≥ 12 y/o.
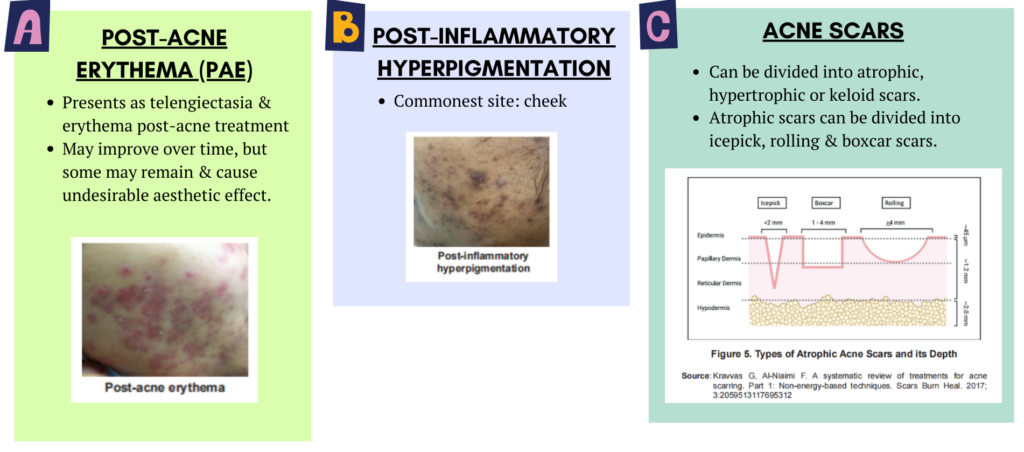
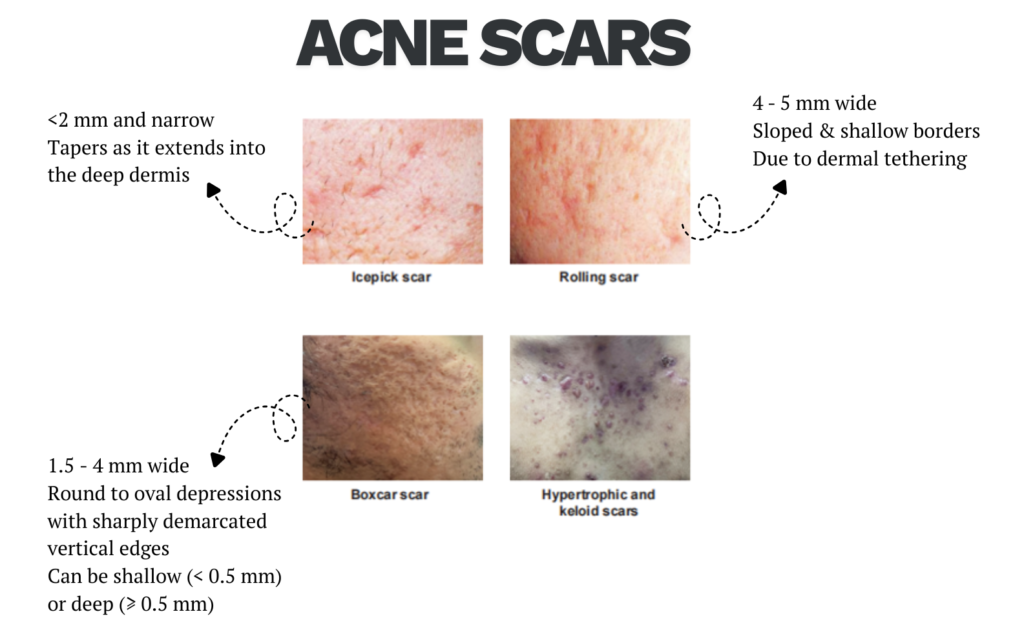
Complications
Referral
Urgent: within 24 hours
- Acne fulminans (rare skin disorder)
– Acute, painful, ulcerating & haemorrhagic form of acne.
+- systemic Sx e.g. fever & polyarthritis
+- bone lesions & laboratory abnormalities. - Urgent referral to PSY if have major depression/exhibiting suicidal behaviour
Seen early: within 2 weeks
- Moderate to severe acne (e.g. nodulocystic acne)
- Severe social or psychological problems including a morbid fear of deformity (dysmorphophobia)
Non-urgent: based on available date
a) Diagnostic uncertainties, e.g.
- Suspected rosacea
- Suspected drug-induced acne
- Suspected occupational causes
- Suspected underlying endocrinological cause (e.g. PCOS) requiring further assessment
- Suspected Staph folliculitis, pityrosporum folliculitis or gram -ve folliculitis
- Rare variants of acne e.g. acne excoriae & chloracne
b) Dermatologist consultation & services.
- Failed oral Abx therapy
- Resistance or intolerance to current treatment
- Scarring or pigmentary changes
- Pregnancy with moderate & severe acne vulgaris
- Indication for specialised physical treatment (e.g. incision, drainage of cysts & laser)
Summary
Mild cases
- Topical bpo – apply in the morning OD, staining of shirt
- Topical retinoid (adapalene) – active lesion with pigmentation, not to be used in pregnancy and lactation, photosensitive – use at night
- Apply moisturizer before/after topical treatment to reduce irritation
- Do not use topical abx as monotherapy
Moderate to severe acne
- Oral abx, review in 6 to 8 weeks, if effective, consider taking for up to 3 to 4 months. Not to be used for more than 4 months. Used with topical bpo and retinoids
- If not responding to systemic abx, refer derm kiv to start isotretinoin.
- Consider start with oral tetracycline group (for more than 8 years above)
- Oral erythromycin can be used for all age group
- Reserved macrolide for pregnant patient
- Oral isotretinoin – only prescribed by dermatologist
Algorithm
Reference
Ministry of Health Malaysia. (2022). Clinical practice guidelines: Management of acne vulgaris (2nd ed.). Malaysian Health Technology Assessment Section (MaHTAS).
