Prevention of gout
- Maintenance of healthy body weight
- Avoid alcohol
- Adherence to Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) which:
– Discourages purine-rich red meat, fructose-rich foods, full-fat dairy products & saturated fat.
– Encourages vegetables, fruits, whole grains, fat-free or low-fat dairy products, fish, poultry, beans, nuts & vegetable oils. - Diuretics should be avoided if possible, or replaced by an alternative drug when used as an antihypertensive agent.
Dietary recommendations🥗
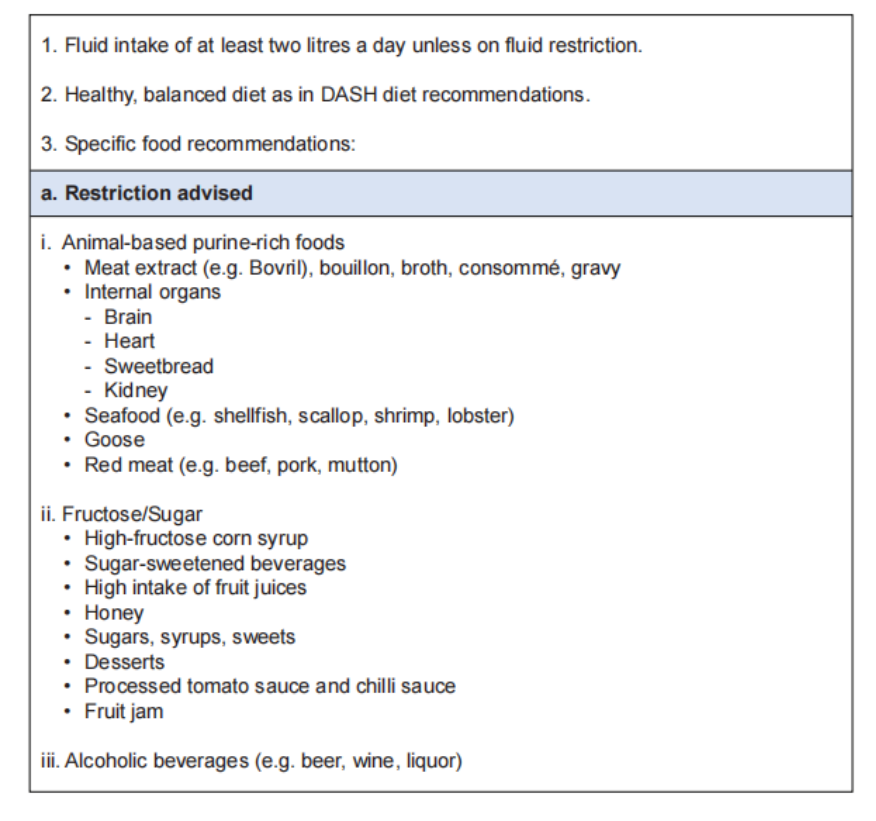
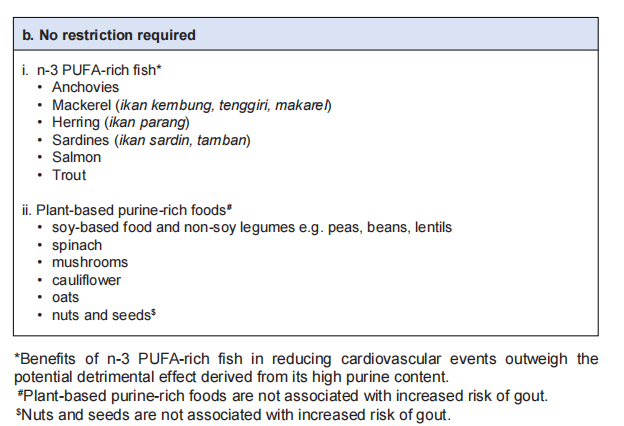
Management of gout flare 🔥
Mainstay of treatment: pain relief
The following monotherapy may be used:
i. Colchicine
ii. NSAIDs/COX-2 inhibitor
iii. Corticosteroids
Combination of the above may be used if response to monotherapy is insufficient
Indications for Urate-Lowering Therapy (ULT)
Established indications:
– Recurrent gout flares (≥ 2 flares in 12 months) OR
– Presence of ≥ 1 tophi OR
– Presence of radiographic damage attributable to gout
Other conditional recommendations for ULT initiation after first gout flares:
– Moderate to severe CKD (Stage ≥ 3) OR
– SU concentration of > 9mg/dL (540 umol/L) OR
– Urolithiasis
Available ULT options
- Xanthine oxidase inhibitors – allopurinol & febuxostat
- Uricosuric agents – benzbromarone & probenecid
– Contraindicated in patient with urolithiasis & are not recommended in severe renal impairment. - Recombinant uricase – pegloticase
- Others – ? Ural sachet
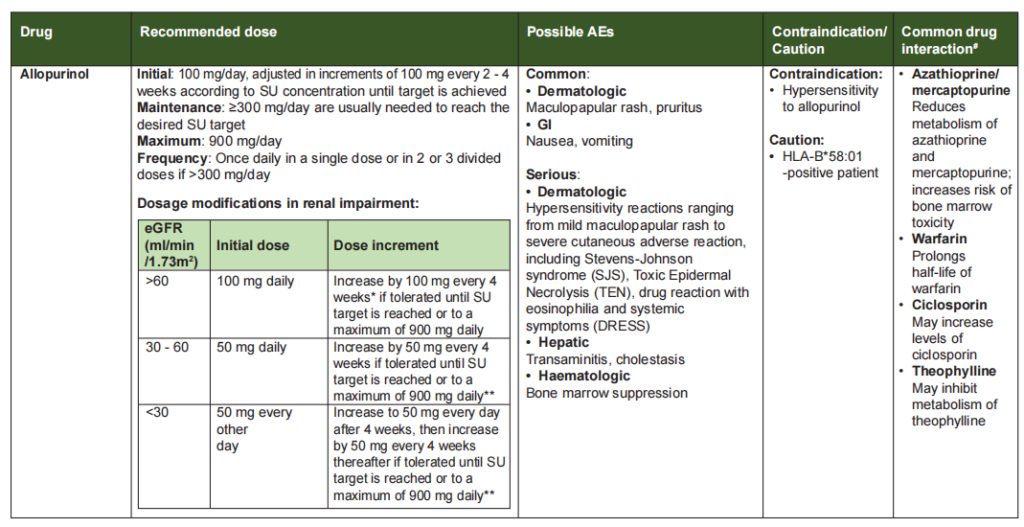
Allopurinol
- 1st line
- Start at low dose & increase gradually.
- Severe cutaneous adverse reaction (SCAR) is the more serious A/E. There was a strong dose-response relationship between starting dose of allopurinol and Allopurinol Hypersensitivity Syndrome (AHS). Therefore always start low, go slow.
- Start low dose 50 mg or 100 mg & increase slowly every 4 weeks.
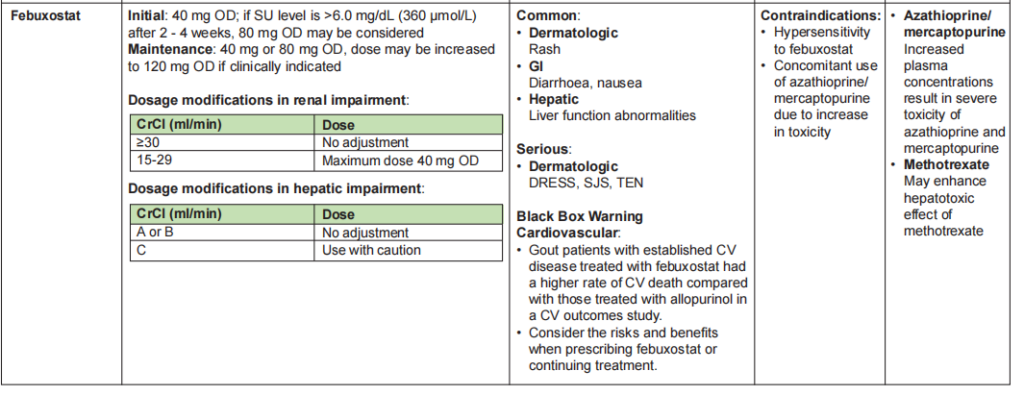
Febuxostat
- 2nd line
- Can be used in patient with renal impairment (eGFR 15 – 89)
Flare prophylaxis
Initiation of ULT leads to dissolution of MSU deposits which causes dispersion of crystals resulting in increased gout flares.
Concomitant anti-inflammatory agents should be started to reduce flares.
Preferred choice: Stepwise dose increase of ULT &/or concomitant colchicine (0.5 mg OD or BD).
Prophylaxis should be used for at least 3 – 6 months when initiating ULT.
Treat-to-Target (T2T) 🎯
Aim for serum urate < 360 umol/L (0.36 mmol/L) should be applied in treatment of all patients.
– A lower SU target of < 5mg/dL (300 umol/L; 0.30 mmol/L) for faster dissolution of crystals is recommended in severe gout (tophi, chronic arthropathy, frequent flares)
– However, some studies have suggested that urate might be protective against various neurodegenerative disease, thus prolonged SU < 3 mg/dL (180 umol/L; 0.18 mmol/L) is not recommended.
Gout in CKD patients
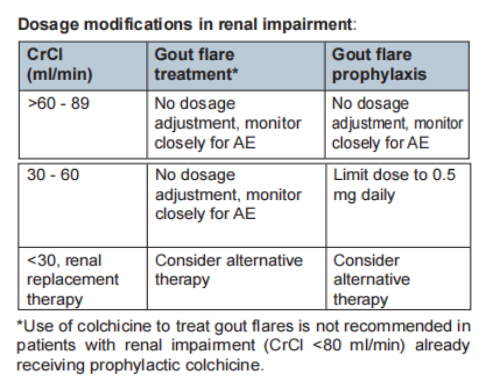
T2T strategy with renal dose adjustment.
ULT: Allopurinol (1st line), Febuxostat (2nd line), Uricosuric agent (contraindicated)
Gout flare: Corticosteroids may be used. Avoid NSAIDs. Colchicine (use with caution). Topical ice therapy safe to use.
Flare prophylaxis: Stepwise dose escalation of ULT, colchicine at reduced dose.