Prognosis of CKD (Depends on 4 factors)
- Cause of CKD
- GFR category
- Albuminuria category
- Other risk factors and co-morbid conditions
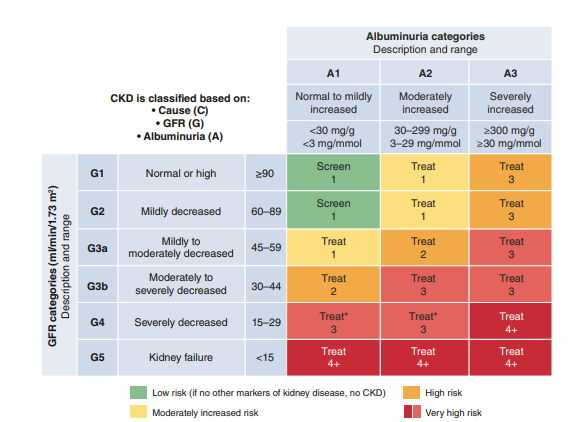
Risk stratification using KDIGO heatmap to guide treatment and follow up.
Clinicians should initiate appropriate management for patients at risk of CKD progression (e.g. BP, DM, dyslipidemia, proteinuria, etc)
The numbers 1, 2, 3 and 4+ suggest the frequency of monitoring (no. of times per year)
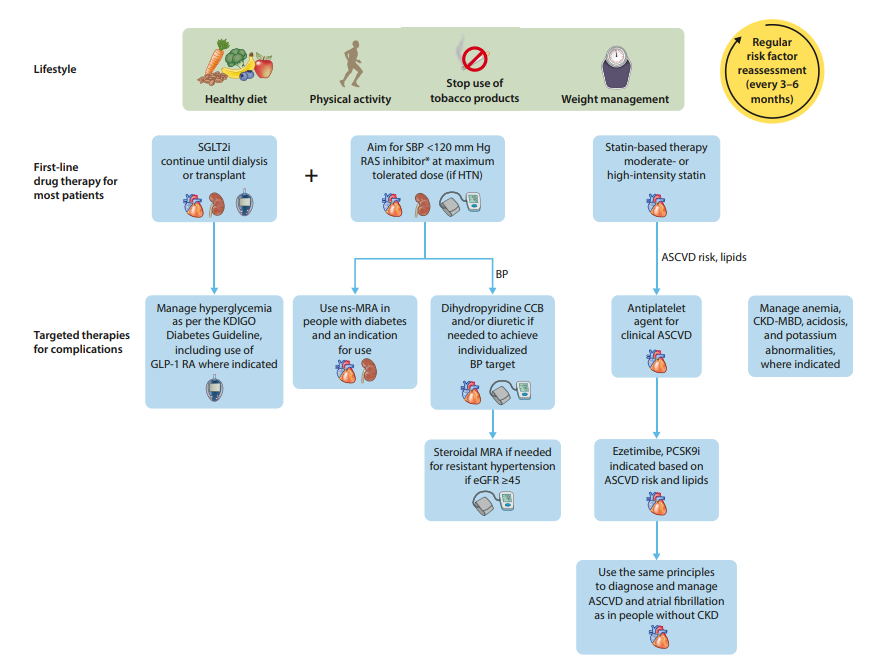
Managing CKD
The aim of CKD treatment is to delay its progression, reduce CV risk and manage CKD-related complications
General measures like lifestyle modification, optimizing other co-morbidities should be incorporated for all patients.
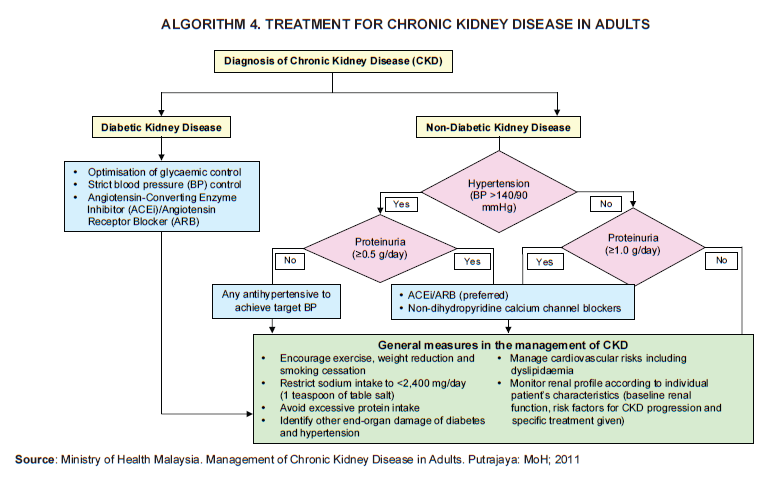
This algorithm is adapted from our Malaysia CPG guidelines on management of CKD. It is has been well known that ACEi/ARB have a major role in the management of CKD and this is evident also from the recommendations by KDIGO 2024.

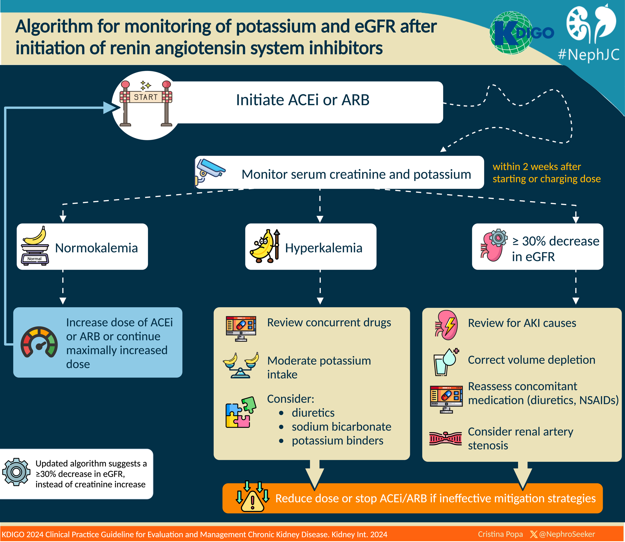
Once ACEi or ARB is initiated, the renal function should be repeated within 2 weeks, to look for any hyperkalemia, significant raised in creatinine and/or decrease if eGFR
SGLT2i
Though it has not been included as part of the algorithm in our Malaysia CPG guidelines yet (but was briefly mentioned in one of the section), I believe it will soon be incorporated in more detail in the coming edition. SGLT2i has been strongly recommended in the KDIGO 2024 guidelines for its role in the management of CKD.

What else? (KDIGO 2024)
1. Nonsteroidal Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist (MRA) – Finerenone
- Appropriate for adults with T2DM who are at high risk of CKD progression & CV events (persistent albuminuria despite treatment).
- May be added to RASi & SGLT2i for treatment of T2DM & CKD in adults.
- Select people with normal serum potassium concentration & monitor serum potassium regularly (risk of hyperkalemia).
2. GLP-1RA
- In patient with T2DM and CKD who have not achieved individualized target despite use of metformin and SGLT2i, or who are unable to tolerate those medication.
Holistic approach (KDIGO 2024 guidelines)